Many organizations use a dedicated local administrator account on each Windows device for support and break-fix. Intune doesn’t include a single “create local admin” configuration profile, but you can create the account in two ways: with a Custom configuration profile using OMA-URI settings (Accounts CSP), or with a PowerShell script deployed via Intune’s PowerShell scripts feature.
This guide walks through both methods: (1) a custom profile with two OMA-URI entries—one to create the local user and set the password, one to add the user to the local Administrators group—and (2) a PowerShell script that creates the account if it doesn’t exist and adds it to Administrators, then deploy that script in Intune.
What You’ll Do
- Option 1: Create a Custom configuration profile with two OMA-URI settings: create the local user (and password) and add the user to the local Administrators group.
- Option 2: Create a PowerShell script that creates the local user (if missing) and adds it to Administrators, then deploy the script via Devices → Windows → PowerShell scripts.
Option 1: Create a Local Admin with OMA-URI
In the Microsoft Intune admin center, go to Devices → Windows → Configuration profiles. Click Create → New policy. Choose Windows 10 and later as the platform and Templates as the profile type. Select Custom and click Create.
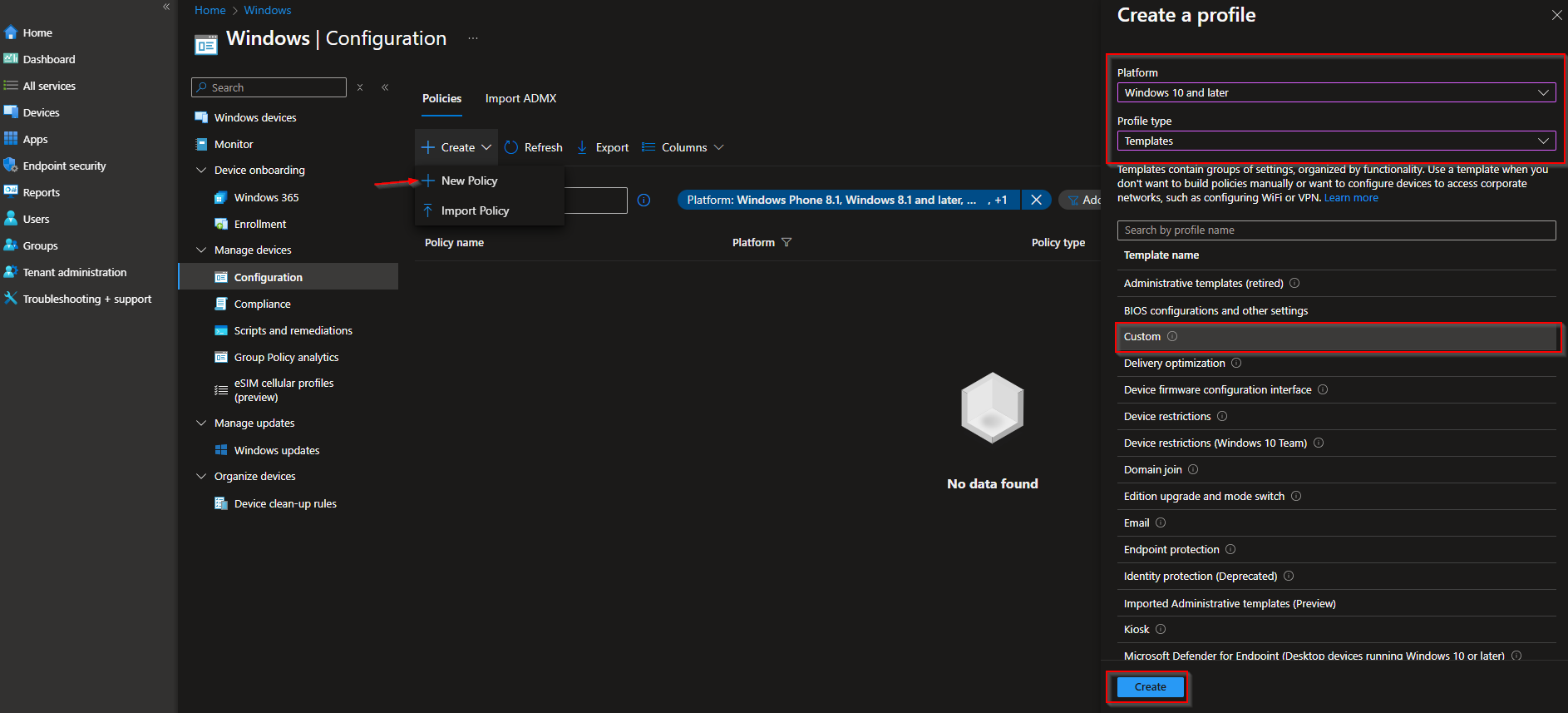
On Basics, give the profile a name (e.g. WIN-Create Local Admin) and optionally a description. Click Next.
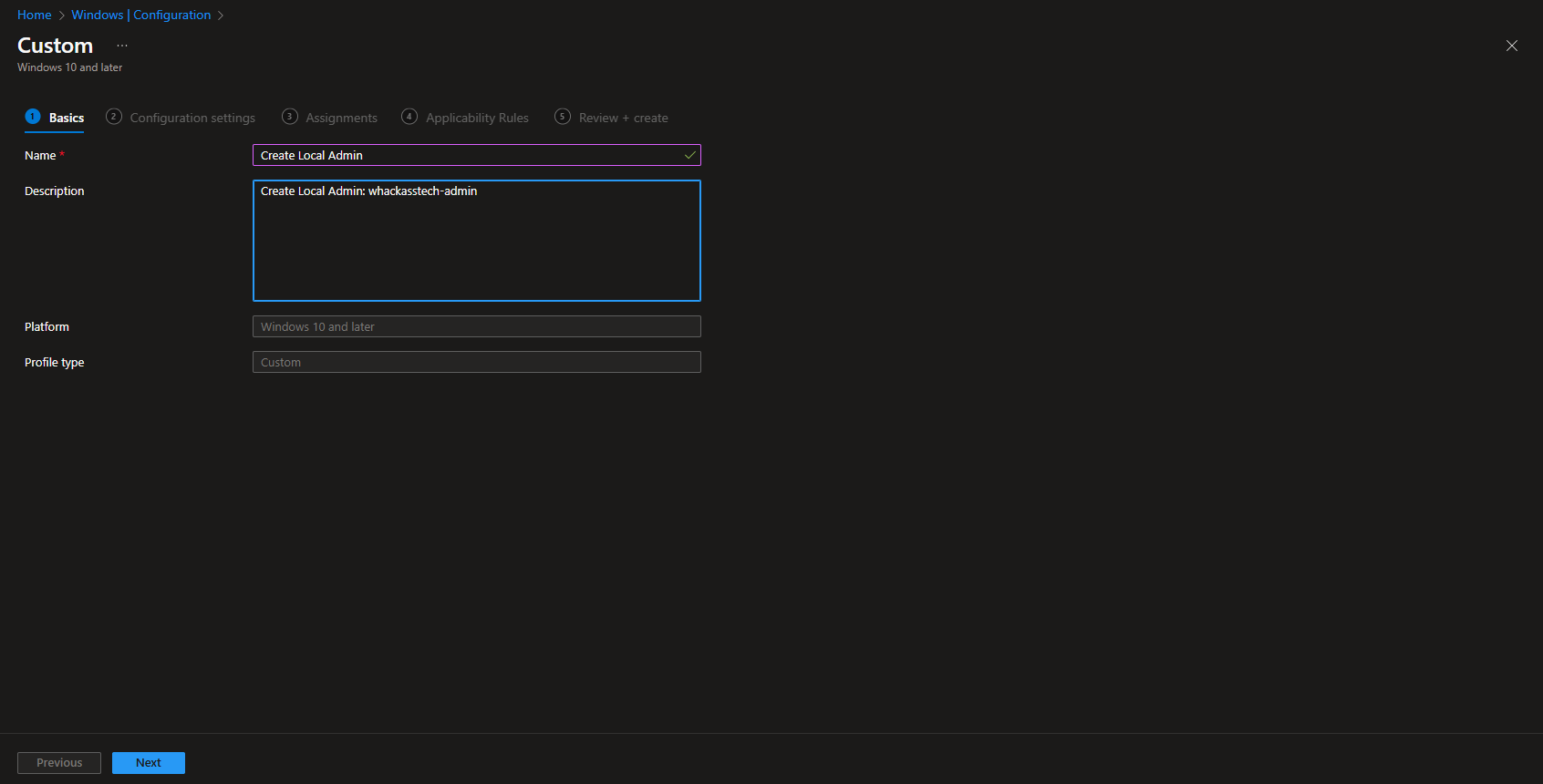
On Configuration settings, add two OMA-URI rows. Use the same local admin username in both URIs (e.g. corp-admin). Replace <LocalAdmin> in the paths below with that name.
Row 1: Create the local user and set the password
- Name: e.g. Create local user
- OMA-URI:
./Device/Vendor/MSFT/Accounts/Users/<LocalAdmin>/Password - Data type: String
- Value: the password for the local admin account (plain text; the CSP applies it)
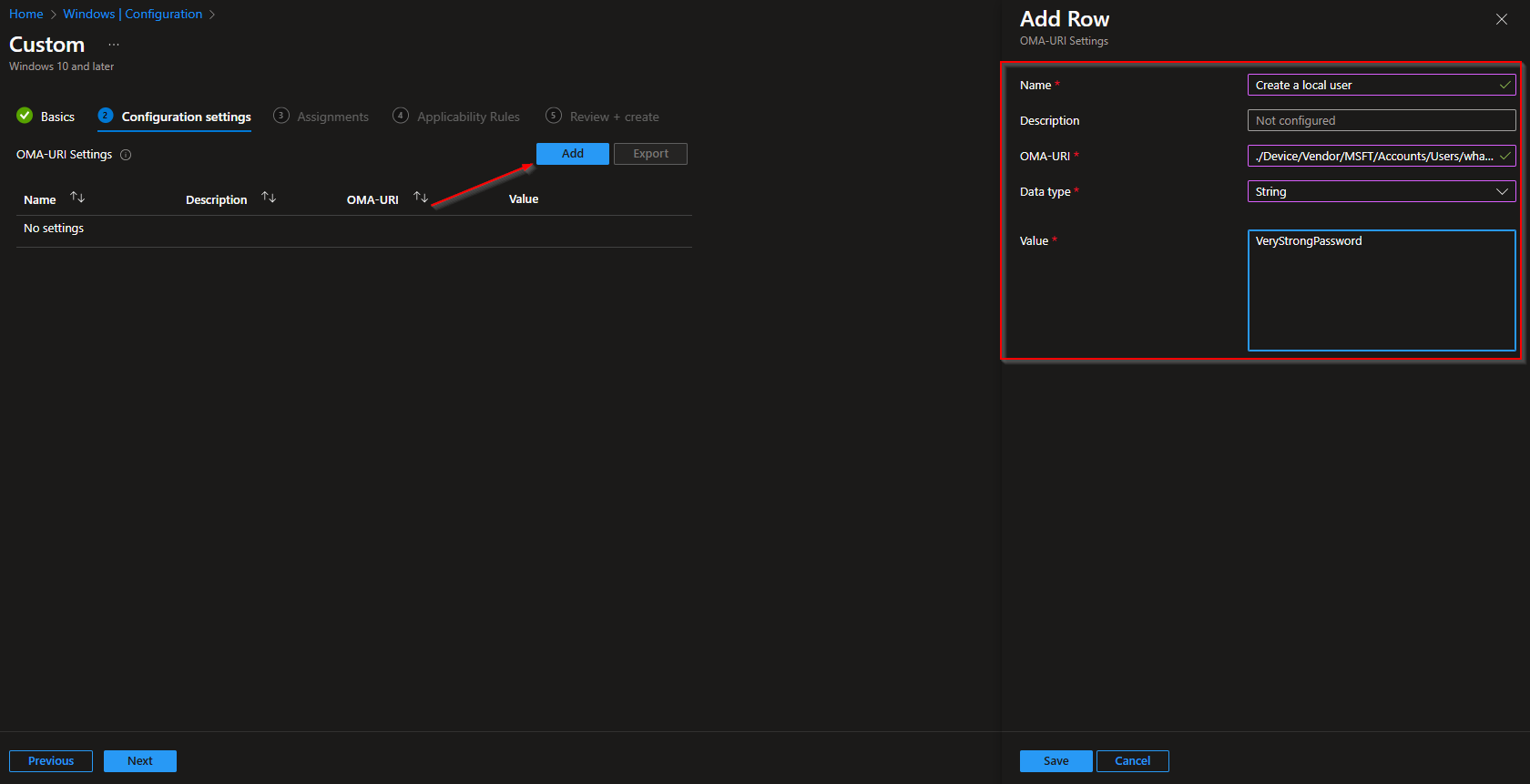
Row 2: Add the user to the local Administrators group
- Name: e.g. Add to local admin group
- OMA-URI:
./Device/Vendor/MSFT/Accounts/Users/<LocalAdmin>/LocalUserGroup - Data type: Integer
- Value:
2(2 = Administrators group)
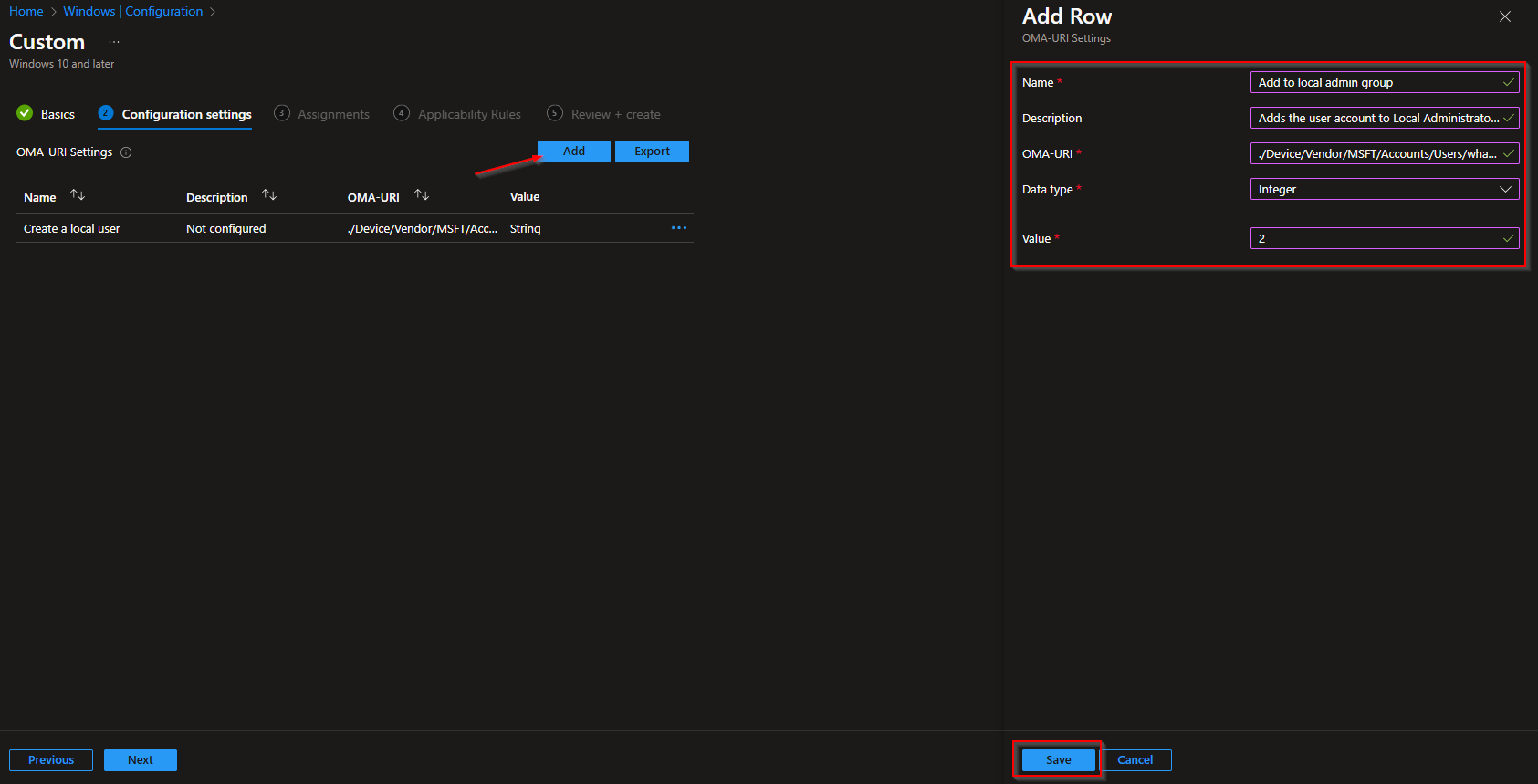
Click Next. Add scope tags if needed, then on Assignments add the groups that should receive this profile (e.g. All Devices or a pilot group). You can skip Applicability rules unless you need them. On Review + create, review and click Create. The same username must appear in both OMA-URI paths. Note: Some tenants report errors in the profile status even when the account is created; check a device to confirm the local user exists and is in the Administrators group.
Option 2: Create a Local Admin with a PowerShell Script
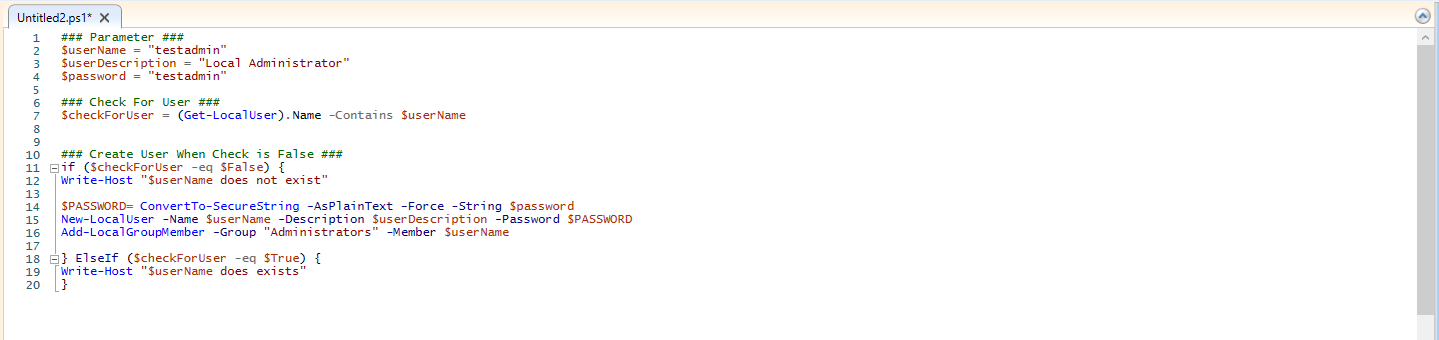
Create a PowerShell script (e.g. CreateLocalAdmin.ps1). The script can check whether the local user already exists; if not, create the user with New-LocalUser and add it to the Administrators group with Add-LocalGroupMember. Run the script in system context (so it can create local accounts). Example (replace [ADMINISTRATOR NAME] and [PASSWORD] with your values):
$userName = "[ADMINISTRATOR NAME]"
$userDescription = "Local Administrator"
$password = "[PASSWORD]"
$checkForUser = (Get-LocalUser).Name -Contains $userName
if ($checkForUser -eq $False) {
$securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force -String $password
New-LocalUser -Name $userName -Description $userDescription -Password $securePassword
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Administrators" -Member $userName
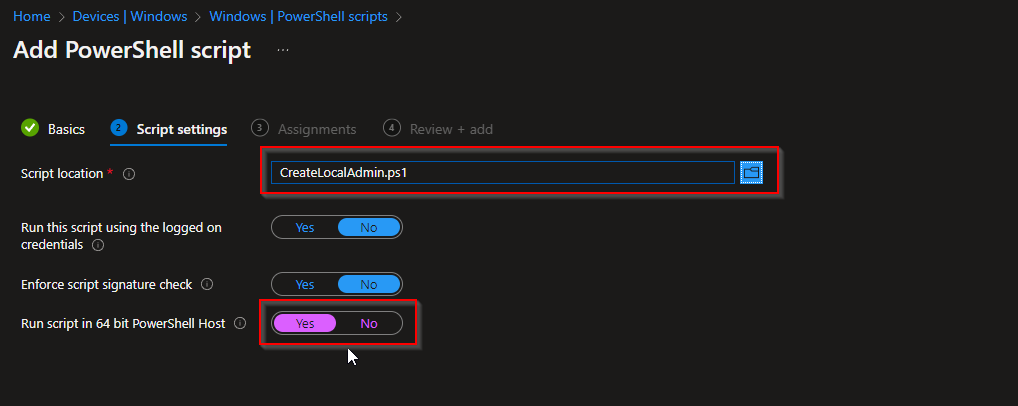
}Save the script. In Intune, go to Devices → Windows → PowerShell scripts → Add. Give it a name (e.g. Create Local Admin), upload the .ps1 file. Set Run this script using the logged on credentials to No (run as system), Enforce script signature check to No, and Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host to Yes. Assign the script to the same groups (e.g. All Devices or pilot). Click Next and Add.
After the script runs on a device, the local admin account exists and is a member of the local Administrators group. You can pair this with LAPS so that Intune manages the account’s password (see below).
Managing the Local Admin Password with LAPS
If you use a custom local admin account (not the built-in Administrator), you can manage its password with Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS). LAPS assigns a unique, strong password per device, rotates it on a schedule, and stores it in Azure AD or Active Directory so authorized admins can retrieve it. After you create the local admin (via OMA-URI or script), configure a LAPS policy in Intune and set the Administrator account name to match the account you created. For steps, see How to configure LAPS with Microsoft Intune.
Wrap-up
You’ve created a local admin with Intune using either a Custom configuration profile (OMA-URI: create user + password, add to LocalUserGroup 2) or a PowerShell script (create user if missing, add to Administrators). Use the same account name in both OMA-URI rows; for the script, run it as system and assign it to the right devices. For stronger security, combine the local admin account with LAPS so passwords are managed and rotated by Intune.