To reduce risk and keep browsers consistent, many organizations restrict which Chrome extensions users can install. Microsoft Intune’s Settings Catalog lets you enforce a Chrome extension blocklist (and optionally an allow list) so only approved add-ons are permitted. This guide covers two approaches: blocking all extensions, or blocking all except a defined set you allow.
What You’ll Do
You will use a single Intune configuration profile (Settings Catalog) for Windows 10 and later and configure:
- Configure extension installation blocklist under Google → Google Chrome → Google Chrome Extensions—with
*to block every extension, or specific IDs to block only those. - Optionally, Configure extension installation allow list in the same category to exempt specific extension IDs from the block (e.g. allow only Bitwarden).
Similar policies exist for Edge and other browsers; this post focuses on Chrome.
Option A: Block All Chrome Extensions
Use this when users should not install any extensions from the Chrome Web Store.
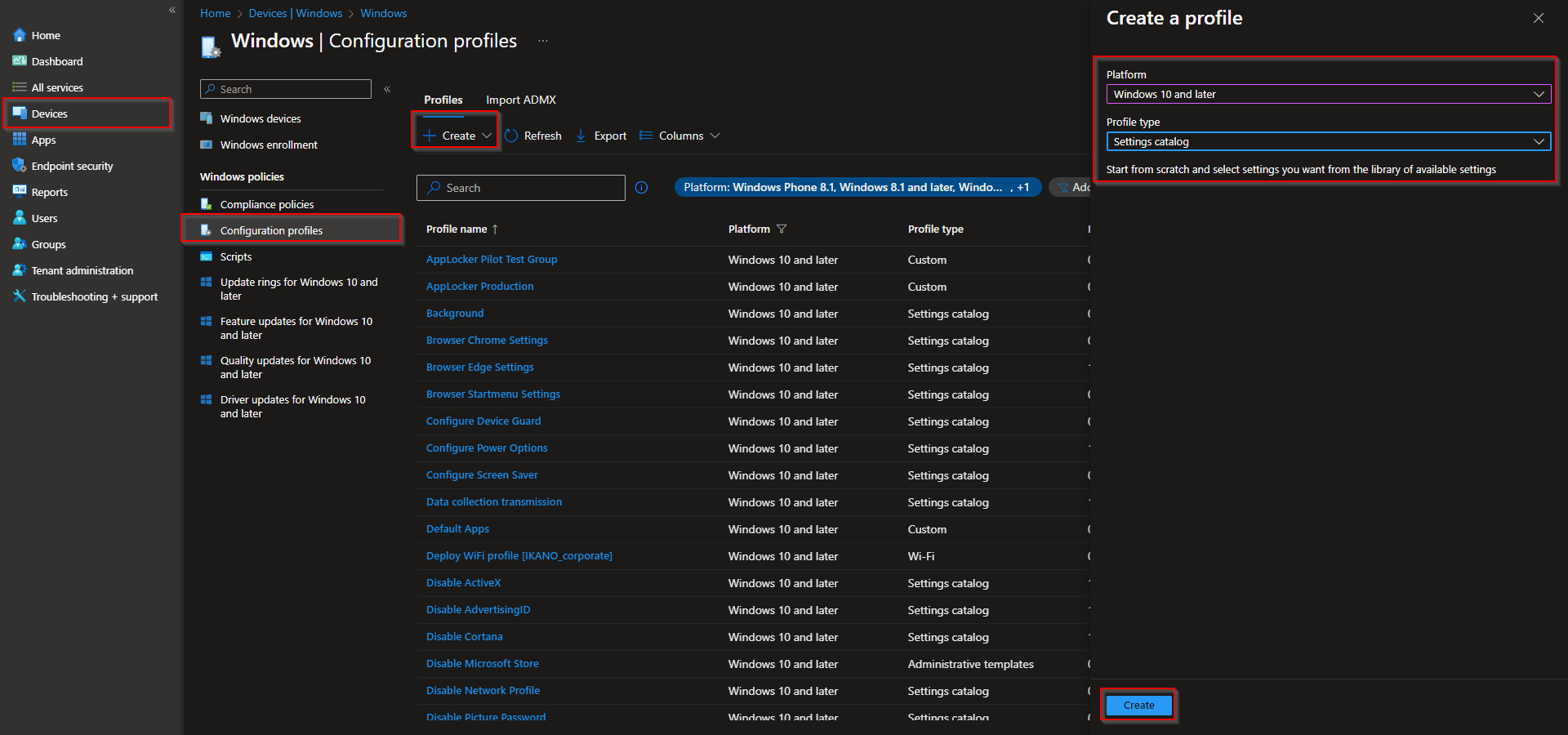
In the Microsoft Intune admin center, go to Devices → Windows → Configuration profiles. Click Create → New policy. Set Platform to Windows 10 and later and Profile type to Settings catalog. Click Create.
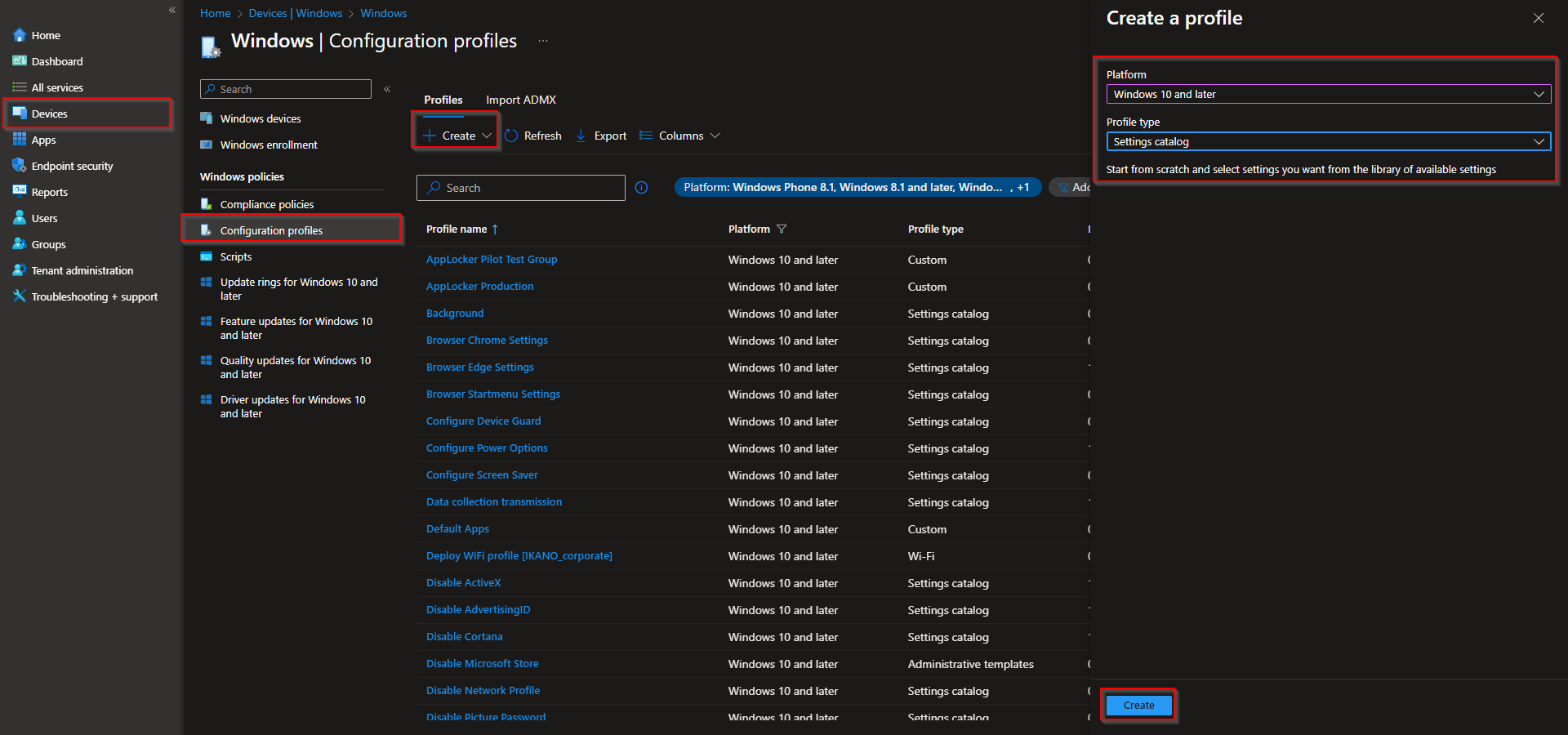
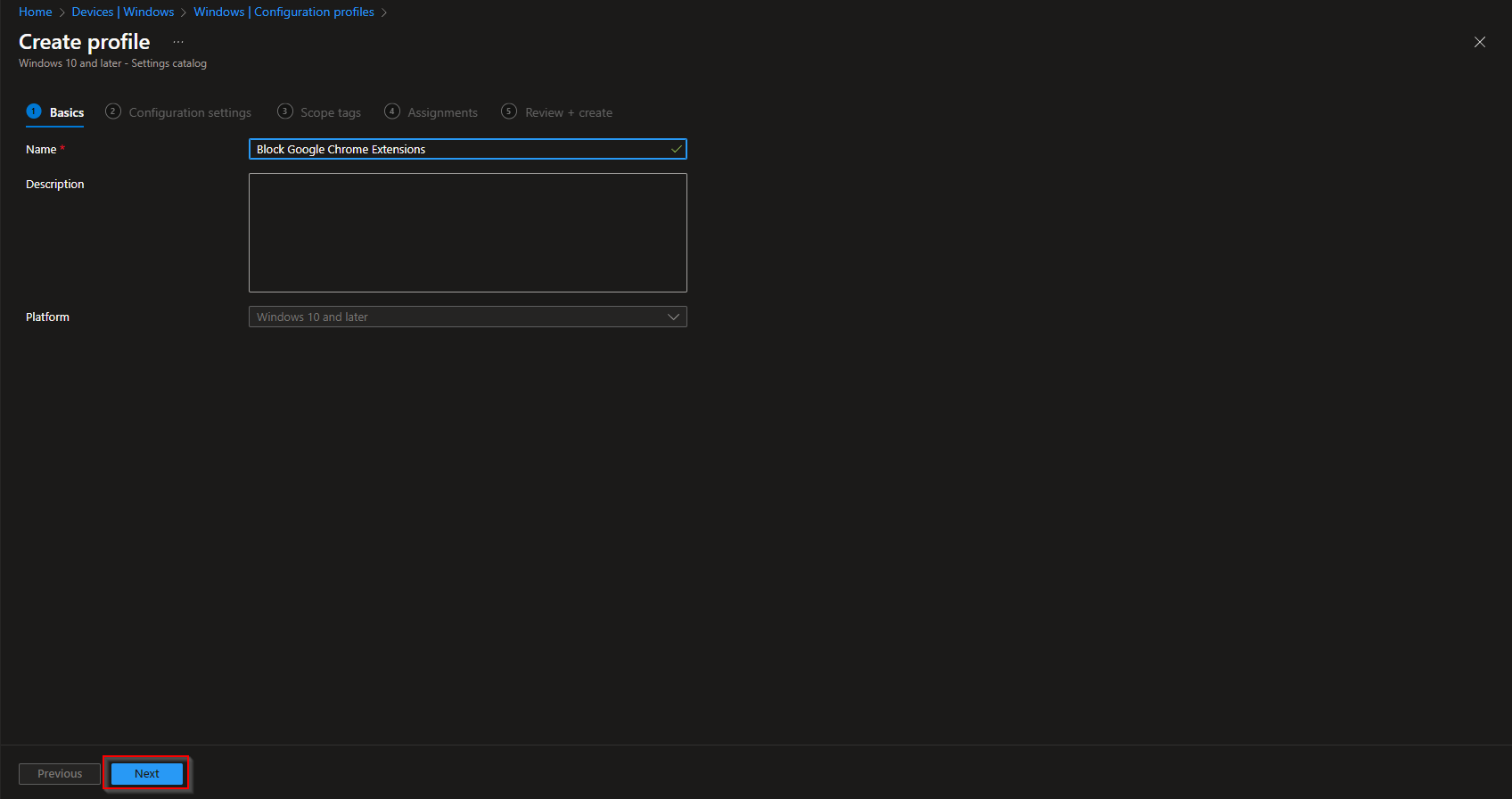
On the Basics tab, enter a Name (e.g. “Block all Chrome extensions”) and optionally a Description. Click Next.
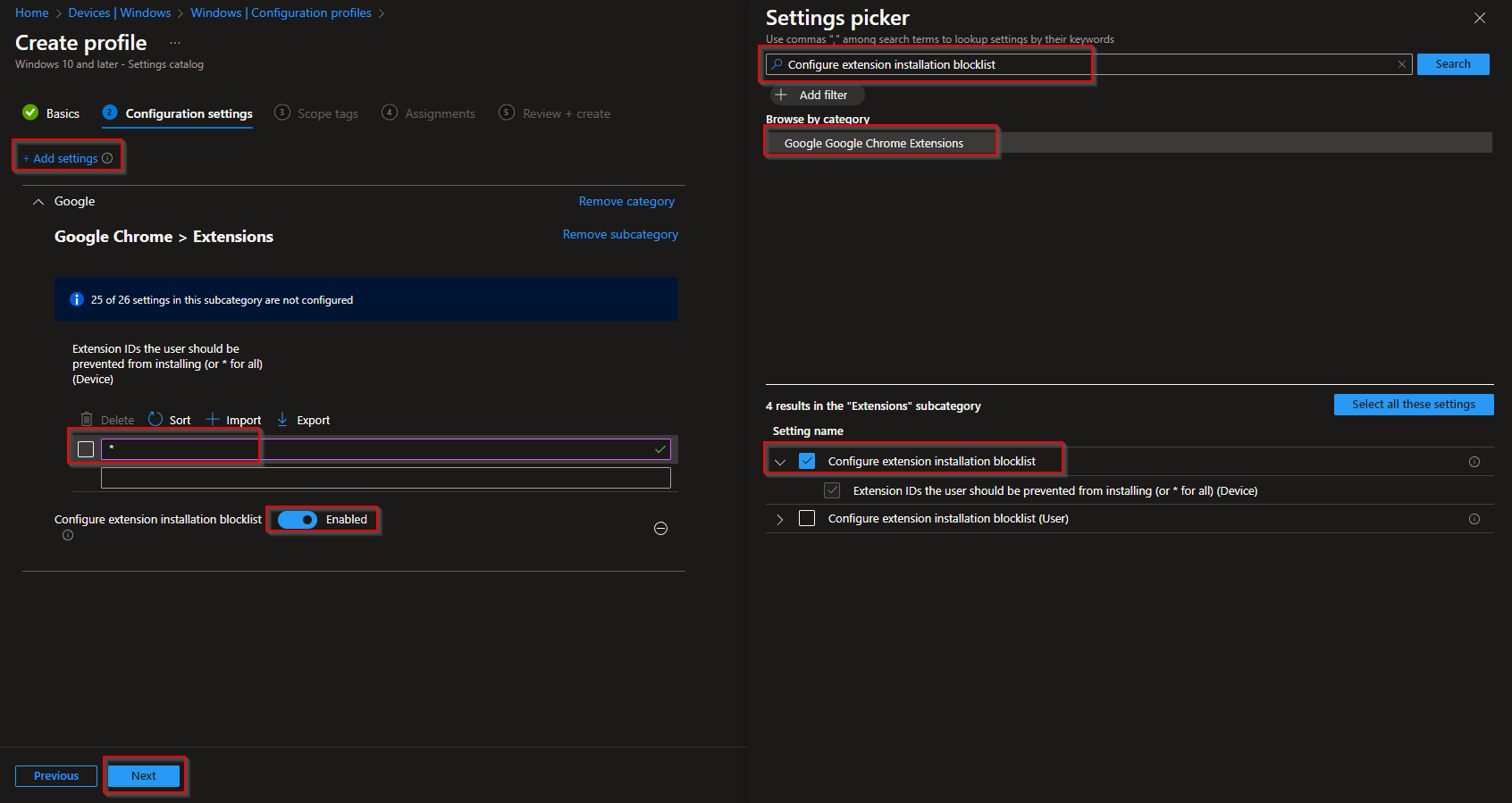
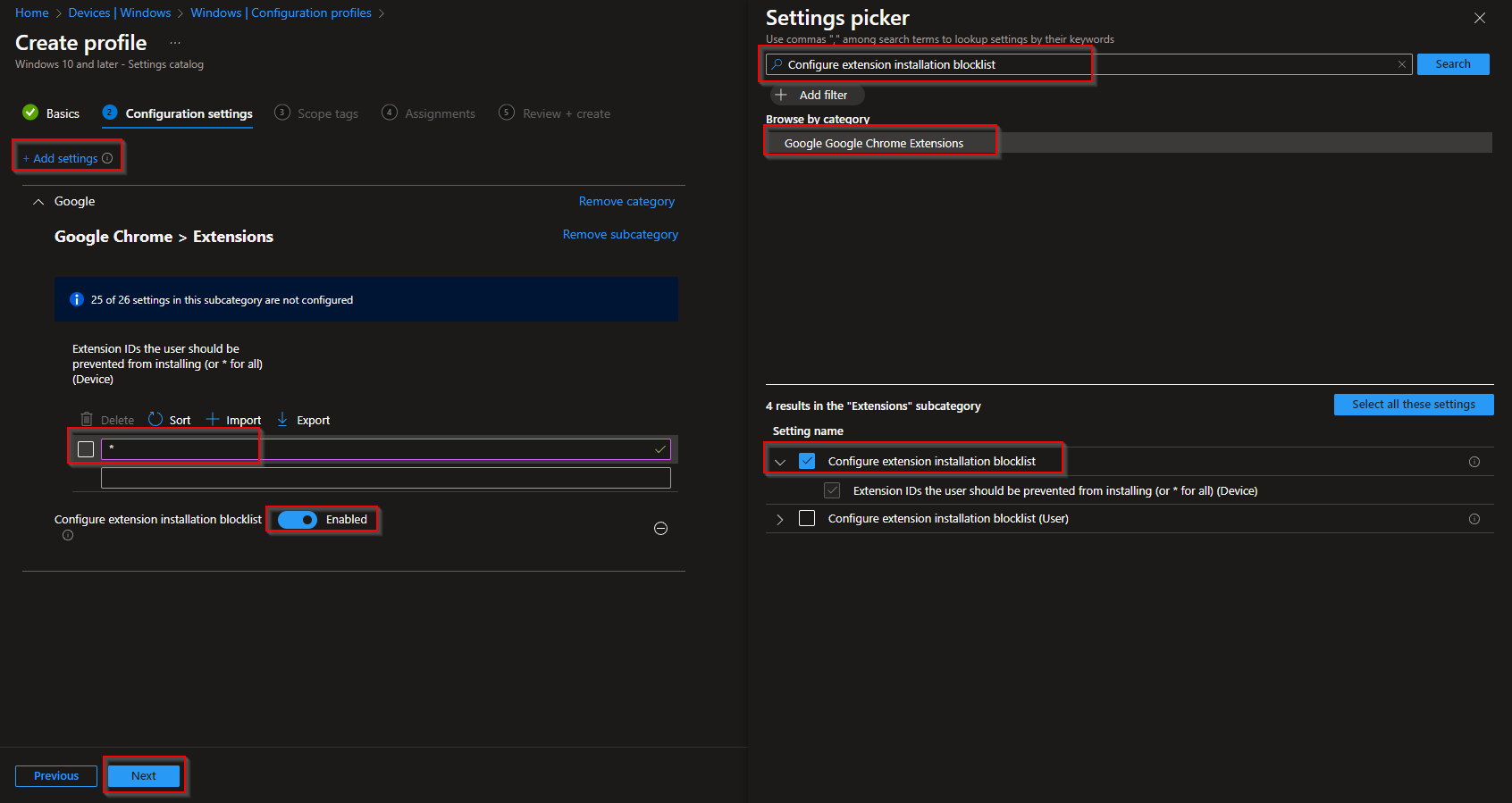
On the Configuration settings tab, click Add settings. Search for Configure extension installation blocklist, expand Google → Google Chrome → Google Chrome Extensions, and add that setting. Enable it and add one row with the ID *. This blocks all extensions. Click Next.
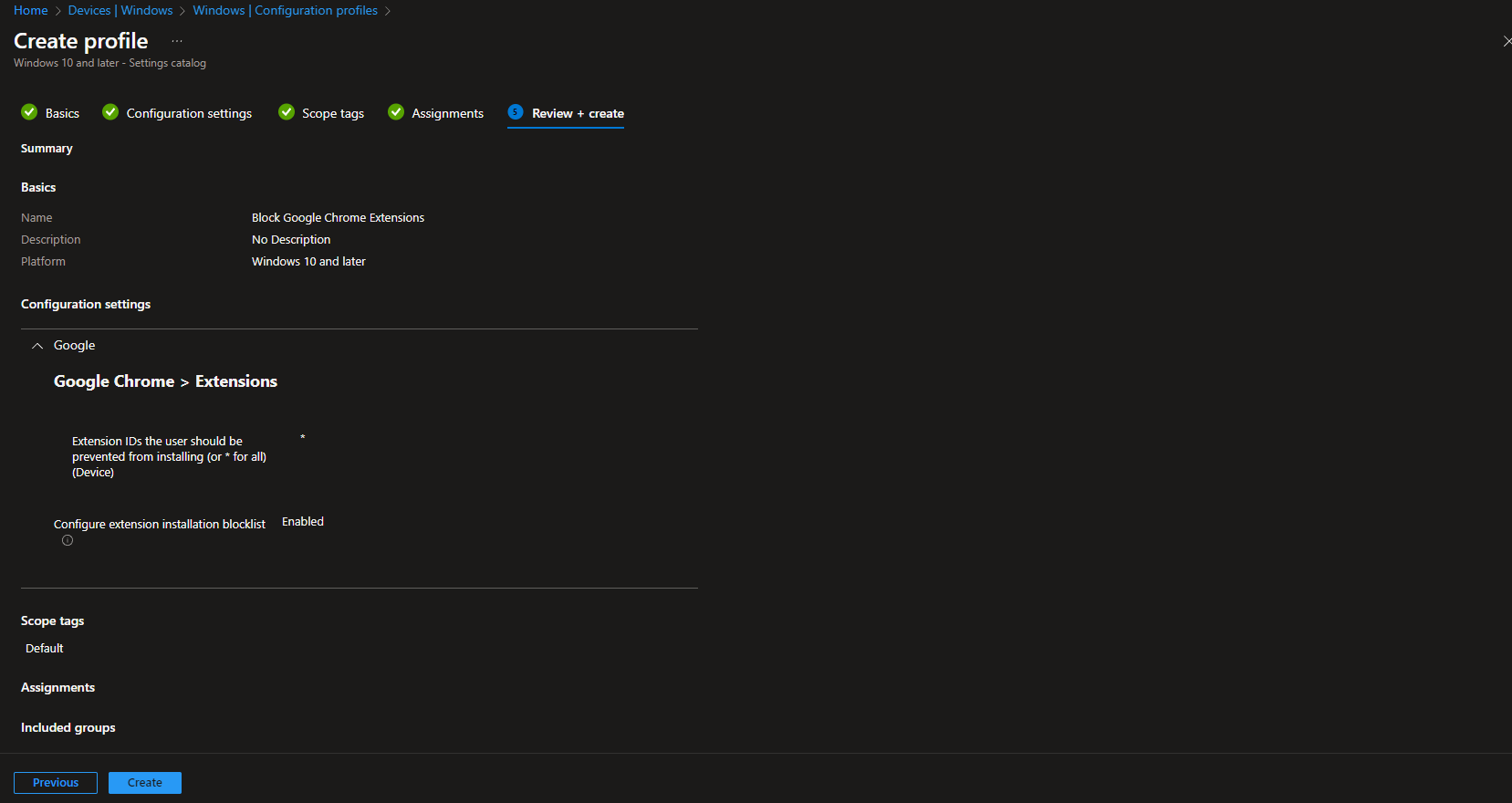
On Scope tags, add tags if needed. On Assignments, add the groups (or All Users / All Devices) that should have this policy. On Review + create, review and click Create.
Option B: Block All Extensions Except Allowed Ones
Use this when you want to block everything except a short list of approved extensions (e.g. a password manager or approved productivity tools). You still set the blocklist to *, then add an allow list with the extension IDs that may be installed.
Get the extension IDs you want to allow
Open https://chromewebstore.google.com/ in your browser.
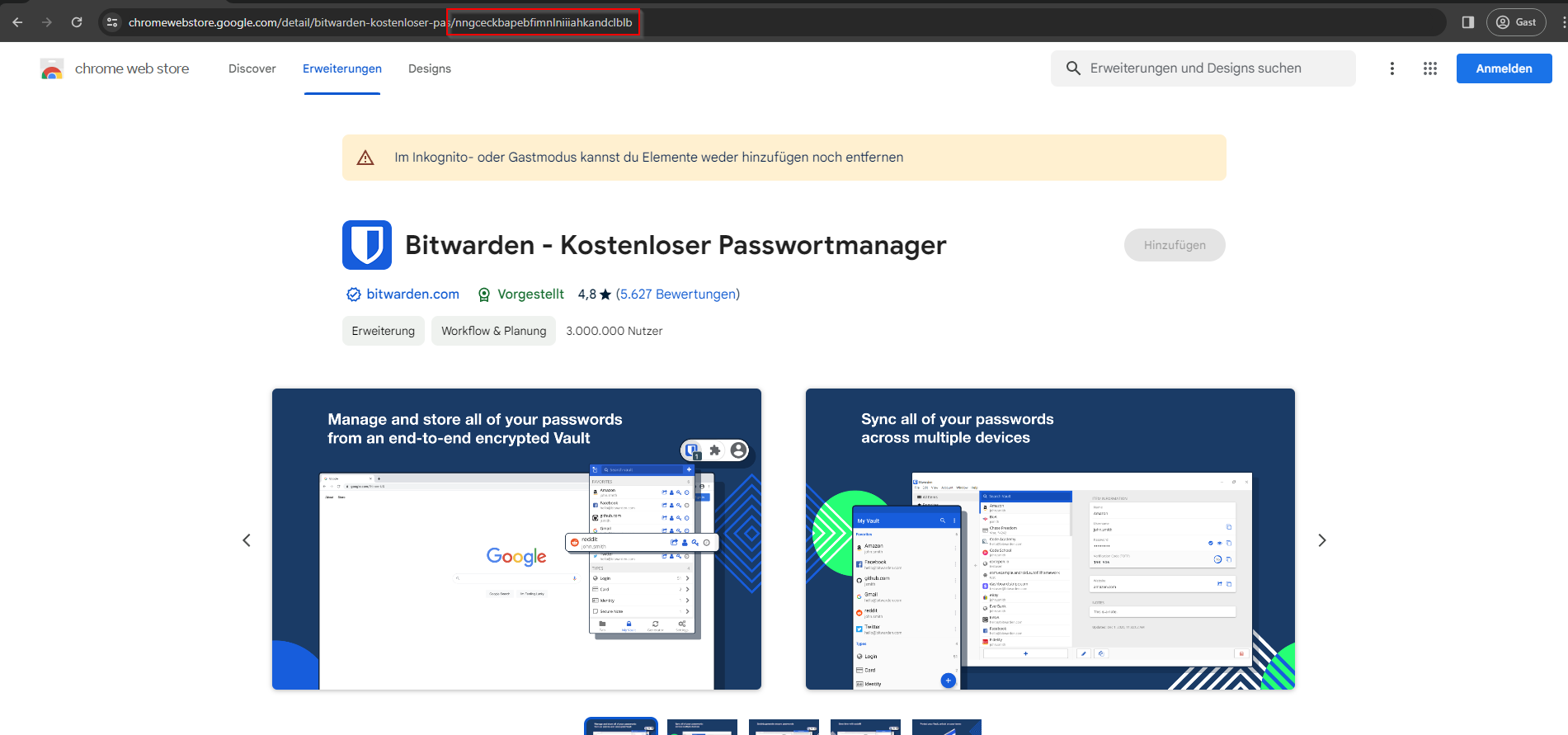
Search for the extension you want to allow (e.g. Bitwarden). Click the extension to open its detail page.
In the address bar, the URL will look like https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/.../XXXXXXXX.... The long string after the last slash is the extension ID (e.g. nngceckbapebfimnlniiiahkandclblb for Bitwarden). Copy that ID and repeat for every extension you want to allow.
Create the profile with blocklist and allow list
Create a new configuration profile as in Option A: Devices → Windows → Configuration profiles → Create → New policy → Windows 10 and later, Settings catalog. On Basics, give it a name (e.g. “Chrome extensions block with allow list”) and click Next.
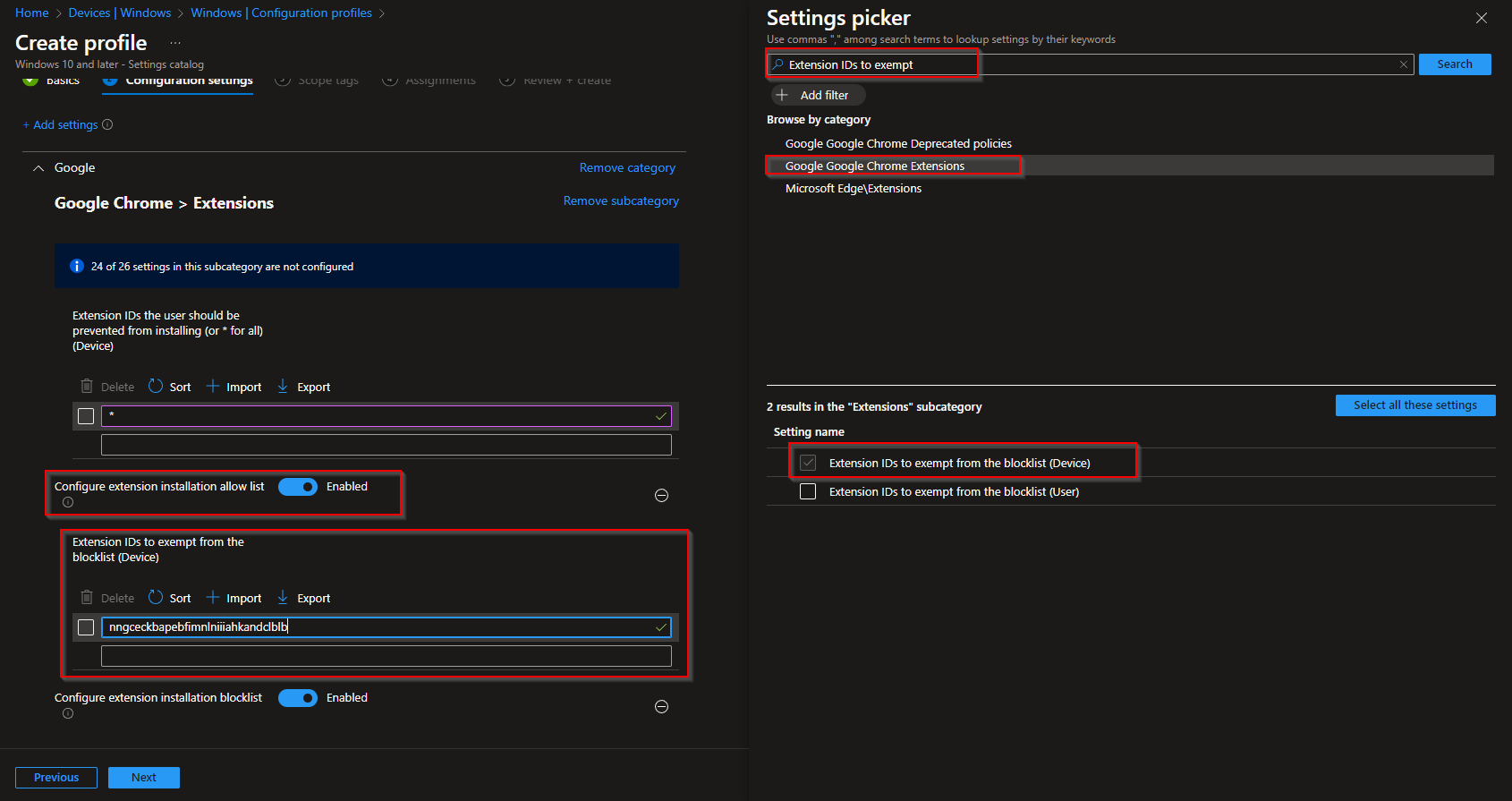
On Configuration settings, click Add settings. Add Configure extension installation blocklist under Google → Google Chrome → Google Chrome Extensions, enable it, and add * so all extensions are blocked by default.
In the same Settings picker, search for Configure extension installation allow list (or “Extension IDs to exempt”). Add it under Google → Google Chrome → Google Chrome Extensions, enable it, and add one row per extension ID you want to allow (e.g. Bitwarden’s ID). Click Next.
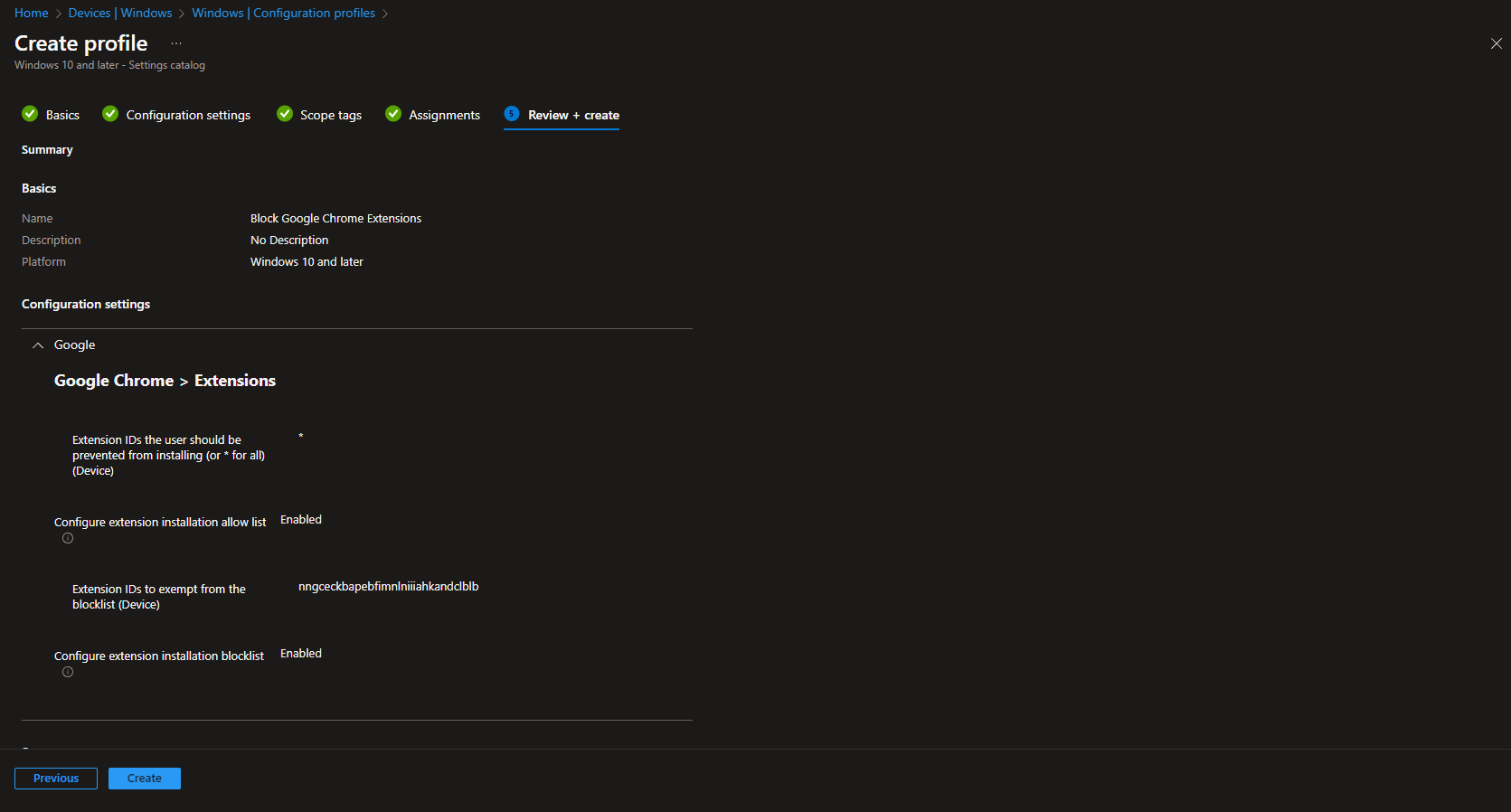
Complete Scope tags and Assignments, then on Review + create confirm both the blocklist and allow list and click Create.
Wrap-up
You can block Google Chrome extensions with Intune by creating a Settings Catalog profile and configuring the extension installation blocklist (use * to block all). To allow only specific add-ons, add the extension installation allow list with the IDs you want to exempt. Assign the profile to the right users or devices to enforce the policy across your organization.